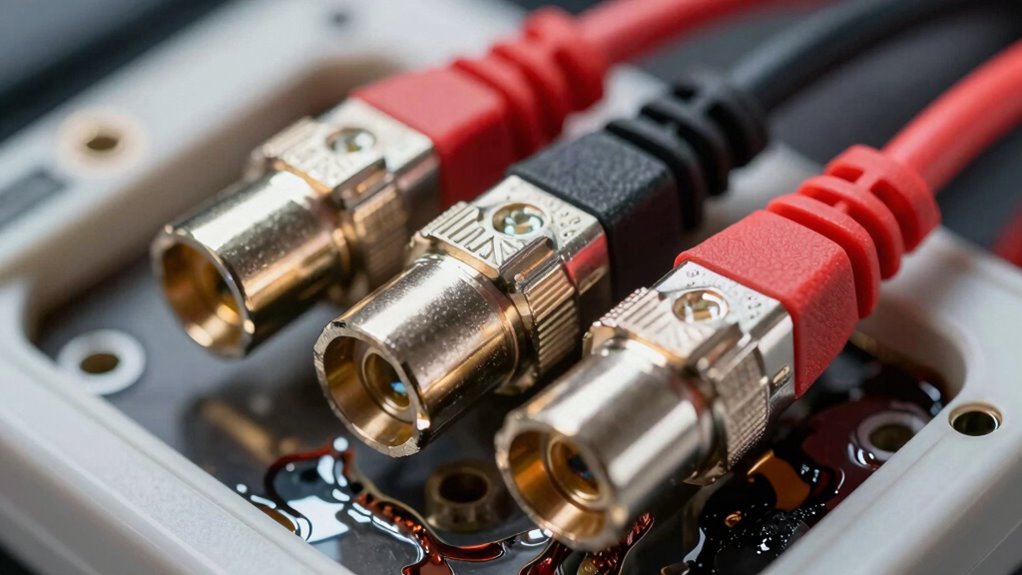
To avoid hot plugs and melted plastic in high-current connectors, guarantee you select components rated for your specific load and use high-quality materials like copper or brass for better conductivity. Properly install connections with secure crimping or soldering, and organize cables to prevent stress or tight bends. Regularly check for signs of wear or looseness. By following these steps, you’ll improve safety and reliability—continue to explore the key practices that keep your system running smoothly.
Key Takeaways
- Use high-quality connectors with appropriate current ratings and durable materials like copper or brass.
- Ensure proper crimping or soldering techniques to secure low-resistance, stable connections.
- Avoid tight bends and sharp kinks in cables to prevent stress and overheating at connection points.
- Organize cables with ties or trays to minimize strain and reduce the risk of disconnection or damage.
- Verify compatibility and adhere to manufacturer specifications to prevent overheating and plastic melting.
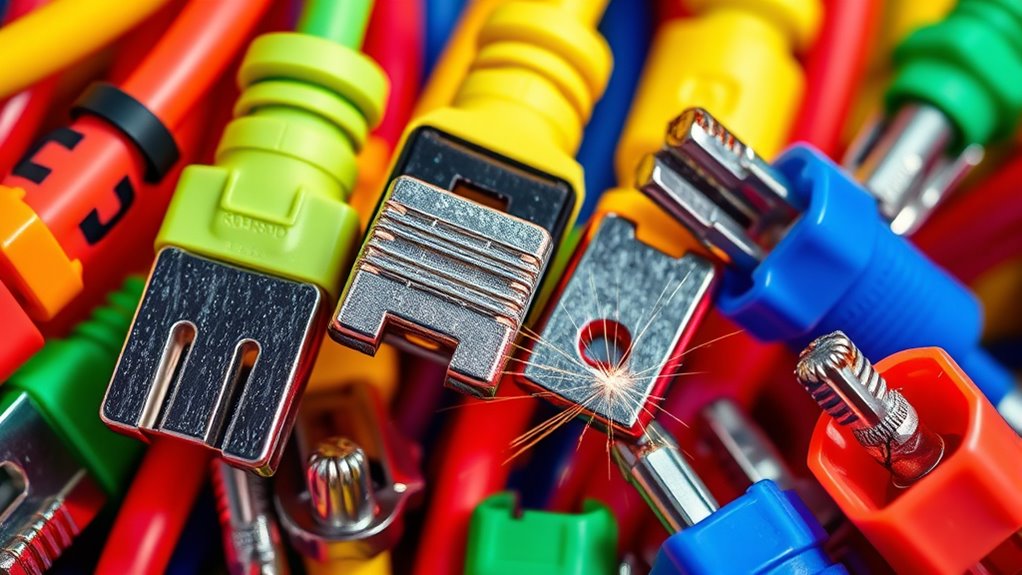

High-current connectors are indispensable components in electrical systems that require the transfer of large amounts of power safely and reliably. When working with these connectors, proper cable management becomes paramount. Poor cable routing or loose connections can lead to increased resistance, overheating, and ultimately, connector failure. To prevent this, you need to organize your cables neatly, avoiding tight bends or sharp kinks that can stress the connector and the wires. Using cable ties, sleeves, or cable trays helps keep everything in check, reducing strain on the connection points and guaranteeing consistent contact. Good cable management not only prolongs the lifespan of your connectors but also minimizes the risk of accidental disconnections or shorts that could cause damage or safety hazards.
Equally important is selecting the right connector materials. High-current connectors are often exposed to significant heat and mechanical stress, so choosing materials with high thermal conductivity and durability is essential. For example, connectors made from high-quality metals like copper or brass with proper plating improve electrical conductivity and resist corrosion, maintaining a reliable connection over time. The insulation and housing materials should also withstand high temperatures without degrading. Thermally resistant plastics or composite materials are commonly used to prevent melting or warping under load. Remember, the quality of connector materials directly impacts how well the connection can handle current loads without overheating or melting plastic parts, which can lead to dangerous hot plugs or system failures.
When installing high-current connectors, always verify that the materials are rated for your specific application. Using connectors with incompatible or substandard materials can result in increased resistance, heat buildup, and eventual failure. Pay attention to manufacturer specifications and ensure that the connectors are designed for the current levels you require. Proper crimping or soldering techniques are also essential to achieve secure, low-resistance connections. If you neglect this, you risk creating gaps or weak points that generate heat, which can cause plastic housings to soften or melt.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Latest Advancements in High-Current Connector Technology?
You’ll find that recent advancements in high-current connector technology focus on thermal management and material innovations. New designs incorporate better heat dissipation features, like advanced cooling channels and heat sinks, to prevent overheating. Material innovations, such as high-performance composites and conductive alloys, improve durability and electrical performance while reducing heat buildup. These improvements help you avoid issues like hot plugs and melted plastic, ensuring safer, more reliable connections under high loads.
How Do High-Current Connectors Compare to Traditional Low-Current Types?
You’ll find high-current connectors differ from traditional low-current ones by using advanced connector materials that withstand higher loads, reducing overheating risks. Their connector insulation is designed to handle heat better, preventing melting and ensuring safety. These enhancements allow for more reliable power transfer, even at high currents, while maintaining durability. Overall, high-current connectors offer improved performance and safety, making them suitable for demanding applications where traditional low-current connectors might struggle.
Are There Industry Standards for Testing High-Current Connector Durability?
Yes, industry standards for testing high-current connector durability exist. You should focus on wear testing to evaluate the connector’s lifespan under repeated use. These standards ensure connectors withstand heat, mechanical stress, and electrical loads over time. By adhering to these protocols, you can identify potential failure points early, helping prevent issues like melting or hot plugs. Following established standards guarantees safety, reliability, and prolonged performance of your high-current connectors.
What Environmental Factors Most Affect High-Current Connector Performance?
Think of your high-current connector as a ship steering stormy seas. Environmental factors like moisture, temperature fluctuations, and pollutants threaten its stability. Corrosion resistance helps prevent rusting, while thermal stability ensures it withstands heat spikes. Exposure to humidity and extreme temperatures can cause performance drops or damage. To keep it sailing smoothly, choose connectors with strong corrosion resistance and thermal stability to battle these environmental challenges effectively.
How Can Users Safely Troubleshoot High-Current Connection Issues?
To safely troubleshoot high-current connection issues, start by inspecting the cable insulation for damage, cracks, or wear. Confirm your connections are tight and stable, avoiding loose or corroded contacts that can cause overheating. Use a multimeter to check for proper voltage and current flow. Always power down the system before handling connectors, and wear protective gear to prevent injury from unexpected sparks or heat.
Conclusion
By understanding how high-current connectors work and following proper installation tips, you can prevent issues like hot plugs and melted plastic. Don’t worry if it seems complex at first—taking your time and choosing the right connectors makes a big difference. With a little care, you’ll enjoy safe, reliable connections that last. So go ahead, upgrade your setup confidently—your equipment and peace of mind will thank you for it.