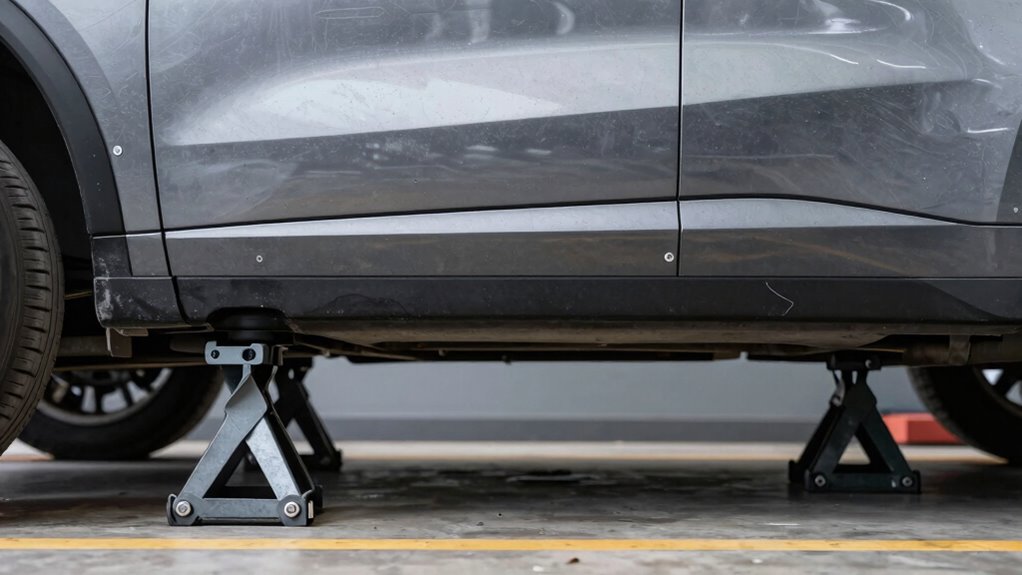
To safely lift your vehicle, always use manufacturer-designated support points like pinch welds, reinforced lift pads, or subframe contact areas. Avoid unsupported parts such as oil pans, control arms, or body panels, as they can crack or bend. verify your jack stands are placed on level ground, aligned properly under reinforced points, and rated for your vehicle’s weight. Proper placement keeps your vehicle stable; continue as you discover essential tips to prevent common mistakes.
Key Takeaways
- Always consult the owner’s manual to identify OEM-reinforced lift points like pinch welds or crossmembers.
- Place jack stands directly under sturdy, reinforced support points, ensuring full contact with the saddle.
- Use firm, level surfaces and wheel chocks to prevent movement or sinking during lifting.
- Avoid unsupported areas such as oil pans, control arms, or unreinforced body panels; support only structural, reinforced points.
- Verify stability by gently lowering onto stands and testing for movement before working underneath.
Recognizing Manufacturer-Designated Jack Points
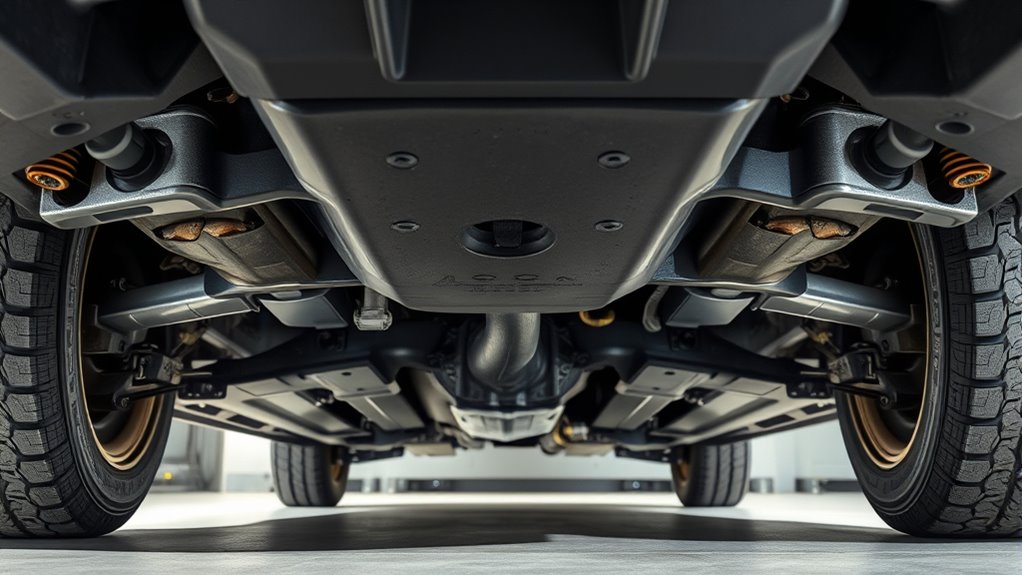

Recognizing manufacturer-designated jack points is essential for safe and effective lifting. Your first step is to consult the owner’s manual, which clearly marks primary lift locations like pinch welds, reinforced lift pads, or subframe nodes. Many vehicles feature stamped notches, welded pads, or reinforced plates under the sill or frame—use these as visual indicators. On unibody cars, placing the floor jack at the center of the subframe or crossmember, halfway between wheels, helps prevent damage to oil pans or suspension components. Additionally, understanding the piercing materials and their placement can further enhance safety during the lifting process. Being familiar with Jack 1023 Jack can provide additional insights into proper jack usage and safety precautions. When in doubt, always refer to factory service information or contact a dealer to confirm the correct jack points and prevent costly or dangerous mistakes. Additionally, understanding the contrast ratio of your projector can significantly improve your home cinema experience by providing deeper blacks and brighter whites, especially in dark scenes. Being aware of vehicle construction details can further enhance safety during the lifting process.
Avoiding Commonly Used but Unsafe Lift Areas
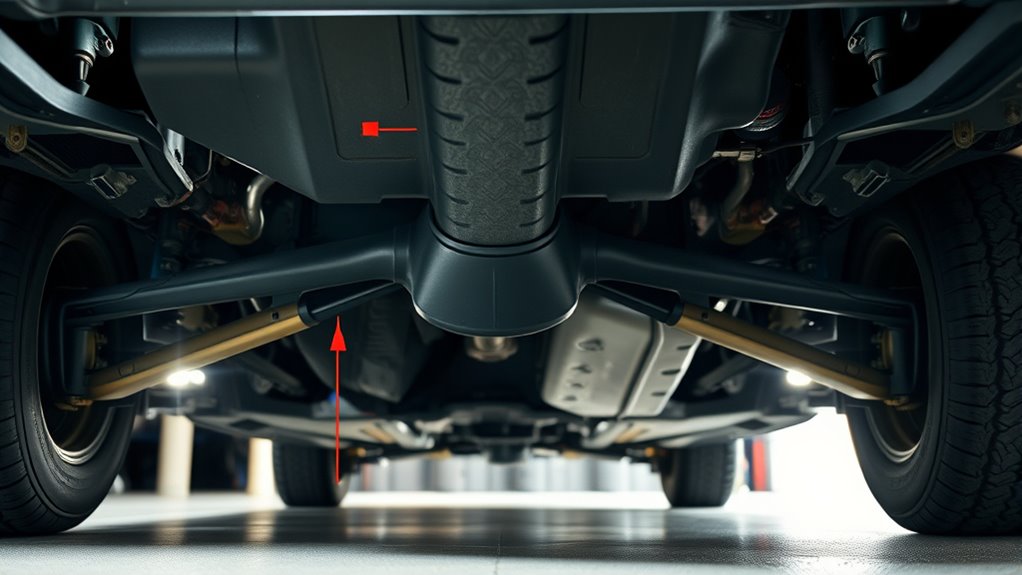
You should never lift or support your vehicle on risky contact zones like oil pans, control arms, or body panels, as they aren’t designed to handle the load. Unsupported body sections, such as filler panels or plastic undertrays, can crack or bend under pressure, leading to dangerous instability. Always focus on solid, reinforced points to guarantee safe and secure jack stand placement. Properly identifying designated lift points is crucial for maintaining vehicle integrity and safety during maintenance. Additionally, selecting energy-efficient cloud servers as part of your infrastructure can enhance overall safety and reliability in your operations. Incorporating professional-grade lifting equipment ensures that you maintain stability and avoid accidents during maintenance, and understanding proper jack stand placement is essential for preventing structural damage or personal injury. Remember, using proper lifting techniques minimizes the risk of vehicle damage and personal injury during repairs.
Risky Contact Zones
Many vehicle owners instinctively lift from areas like the oil pan, control arms, or body panels, but these zones are unsafe for support. These contact zones aren’t designed to bear the vehicle’s weight and can crack, bend, or fail unexpectedly. Using these areas risks damaging critical components or causing accidents. Instead, stick to OEM lift points or reinforced chassis areas. Here’s a quick guide:
| Contact Zone | Why It’s Risky | Better Alternative |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Pan | Prone to puncture or crack under load | Subframe or pinch welds |
| Control Arms | Sensitive suspension parts, not load-bearing | Reinforced lift pads on chassis |
| Body Panels | Thin metal, rust-prone, easily deformed | OEM pinch welds or frame points |
| Exhaust Components | Fragile, heat-sensitive, unsupported | Structural frame or crossmembers |
| Aftermarket Bodywork | Not designed for support, can crack | OEM reinforced jacking points |
Additionally, many vehicles feature designated lift points that are specifically reinforced to safely bear the weight during maintenance. Proper lift point selection is crucial to avoid unnecessary damage and ensure safety during vehicle servicing.
Unsupported Body Sections
Unsupported body sections are frequently misused as lift points despite being unsafe for vehicle support. You should never lift or support a vehicle from areas like the oil pan, control arms, exhaust system, or body panels. These parts aren’t designed to bear weight and can crack, deform, or puncture under load. Using unreinforced sheet metal, filler panels, or plastic trim as support points is risky because they lack structural strength. Instead, focus on OEM-recommended lift points such as pinch welds, reinforced pads, or designated chassis supports. Placing stands on unsupported body sections can lead to sudden failure, vehicle instability, or accidents. Always verify the manufacturer’s guidelines, and avoid improvising support locations to ensure safety for you and your vehicle.
Identifying Reinforced Support Structures on Your Vehicle
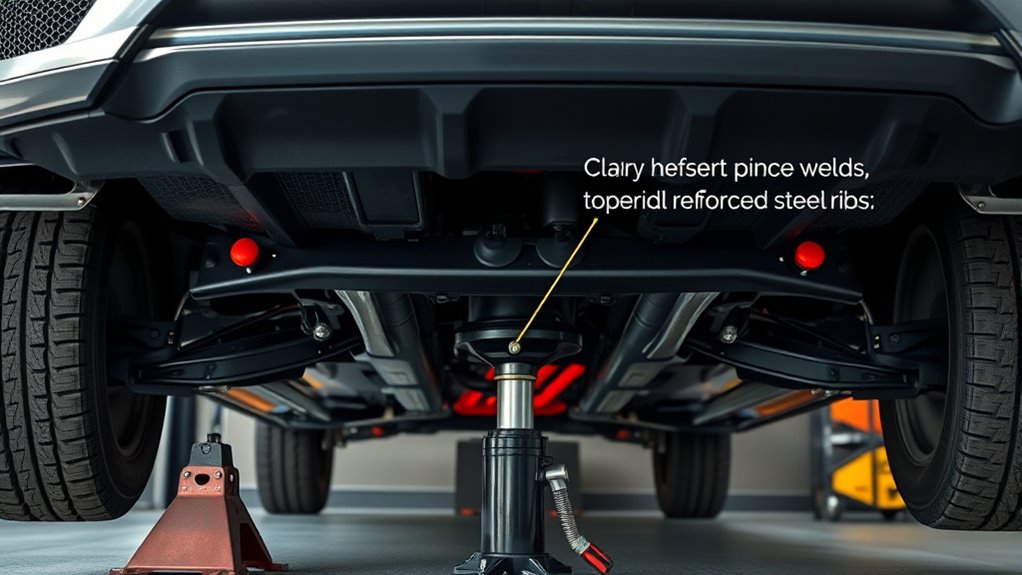
Look for visible reinforcement features like stamped notches, welded pads, or reinforced plates under the sills or frame, which indicate strong support points. Your owner’s manual provides specific guidance on primary jack locations, so check it for manufacturer-specified lift points. Confirm these features prior to placing your jack stands to guarantee safe and reliable support. Additionally, understanding AI-powered virtual reality in e-learning can help you visualize proper lifting points in a simulated environment for better safety awareness. Incorporating water safety practices can also help prevent accidents and ensure secure lifting procedures. Recognizing key traits of successful quality assurance engineers can further enhance your approach to safety and thoroughness in vehicle maintenance.
Visible Reinforcement Features
Reinforced support structures on your vehicle are designed to withstand lifting and support loads safely, and they are often visible through specific features. Recognizing these features helps verify you’re placing jack stands correctly. These features are crucial for ensuring safety during lifting and preventing damage to your vehicle’s structure. 1. Stamped Notches or Cutouts: Look for stamped or embossed marks that indicate reinforced areas, typically located along the rocker panels or frame rails. 2. Welded or Reinforced Pads: Check under the sill or frame for welded pads or thickened metal plates that serve as support points. 3. Visible Structural Ribs**: Observe for thicker metal ribs or gussets that run along the chassis, highlighting strong support zones. Incorporating vehicle support features** into your inspection routine helps confirm proper jack placement and enhances overall safety. Using these features guarantees your vehicle’s weight transfers safely to the support structure, reducing risk of damage or collapse.
Owner’s Manual Guidance
Your vehicle’s owner’s manual provides essential guidance for identifying reinforced support structures, ensuring you’re placing jack stands safely and accurately. It highlights specific locations like manufacturer-specified pinch welds, reinforced lift pads, or subframe points designed to handle load. Many manuals include diagrams or photos showing these support areas, often with stamped notches, welded pads, or reinforced plates visible beneath the vehicle’s body or frame. If your manual mentions a particular support point, follow it precisely—never improvise or rely on guesswork. For unibody cars, the manual might recommend placing jack stands at the center of the subframe or crossmembers. Always cross-reference these points with visible structural features to confirm they’re suitable for lifting, preventing potential damage or failure.
Proper Placement of Jack Stands for Stability
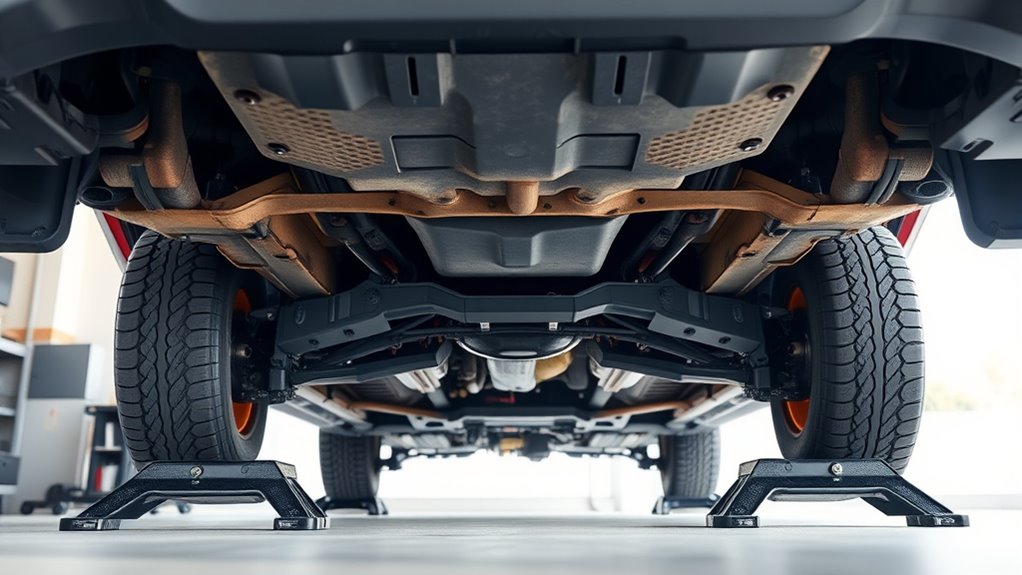

Ensuring proper placement of jack stands is essential for vehicle stability and safety during maintenance. You need to position the stands directly under solid, reinforced points to prevent slipping or tipping. You must first locate the manufacturer-specified lift points, such as pinch welds or reinforced subframes. Second, place the stands upright, centered under these points, ensuring they sit flat on a firm, level surface. Third, adjust the stands to match height, keeping them symmetrical on each side for balanced load distribution. Make sure each stand’s saddle fully contacts the load point without tilting. Confirm that the base is stable on the ground, free of slope or soft spots. Proper placement ensures the stands support the vehicle securely, reducing the risk of collapse or shifting during work. Additionally, verifying that your vehicle is on a level surface helps maintain proper balance and safety. Regularly inspecting your lifting equipment for signs of wear enhances overall safety during maintenance tasks. Maintaining proper placement is especially important when working on uneven terrain or soft ground, as it can significantly impact stability. Always use appropriate safety gear such as gloves and eye protection when working underneath your vehicle. Also, understanding the correct placement of jack stands can help prevent accidents and ensure stability throughout the repair process.
Choosing the Right Stand Capacity and Type
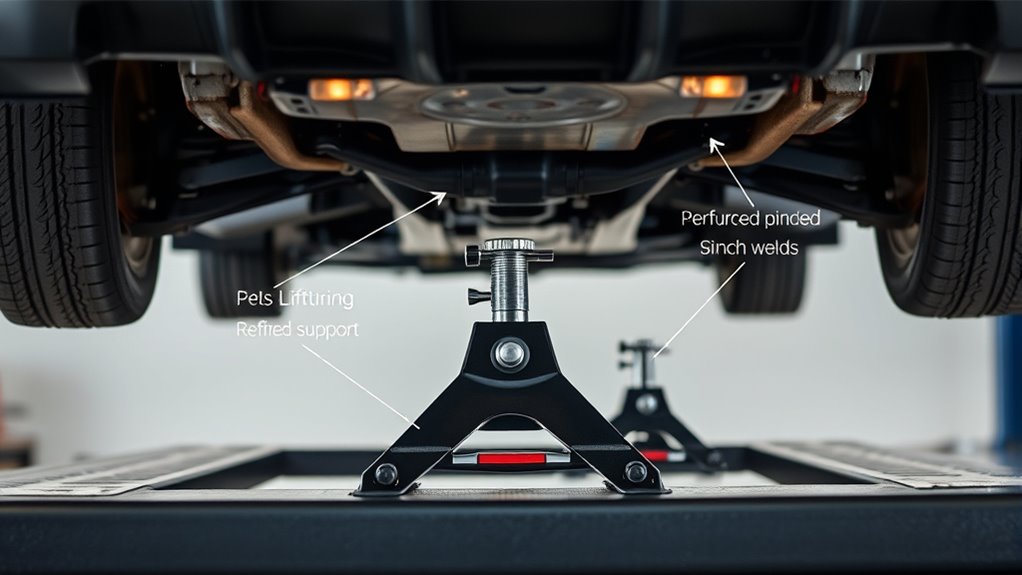
Choosing the right stand capacity and type is essential to safely support your vehicle during maintenance. First, check your vehicle’s gross weight, typically listed on the door frame or owner’s manual, and select stands with a combined rated capacity equal to or greater than that weight. Use stands rated per ASME/ANSI standards to guarantee quality. For stability, opt for wide-base tripod or quad-leg stands, especially on uneven surfaces. Decide between pinned or ratchet stands: ratchet models allow quick adjustments, while pinned stands are more vibration-resistant but require full engagement. Always inspect stands for damage, corrosion, or missing parts before use. Never exceed the rated capacity, and choose stands that match the load’s placement, ensuring they provide solid, reliable support throughout your maintenance work.
Preparing the Surface for Safe Support
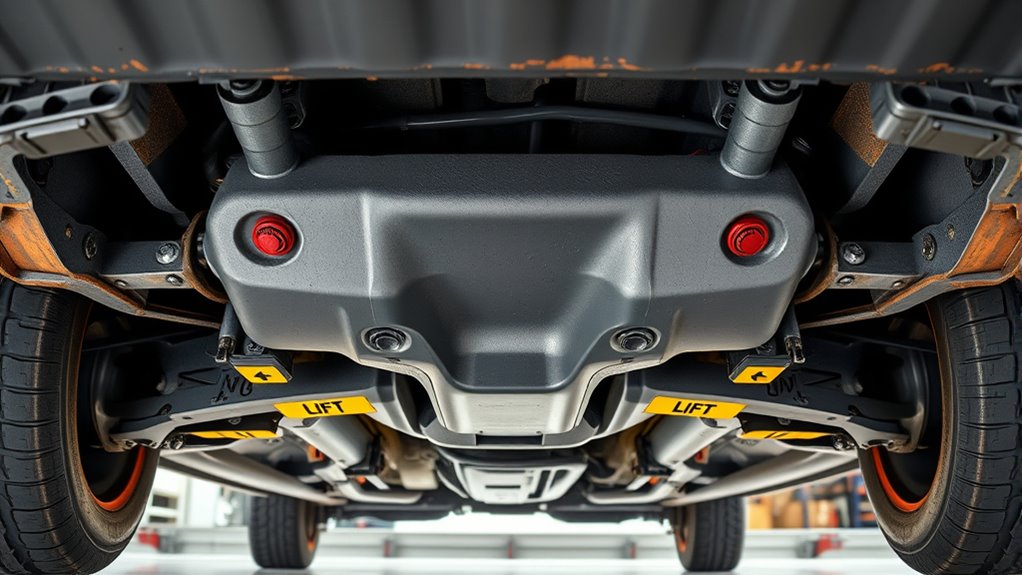

A stable, level surface is essential before placing jack stands to support your vehicle safely. Proper surface preparation prevents slipping, tipping, or uneven load distribution. First, ensure your vehicle is parked on firm, solid ground like concrete or asphalt—avoid soft or uneven surfaces. Second, use wheel chocks on the wheels remaining on the ground to prevent rolling. Third, if the foundation isn’t firm, block or crib the jack base with sturdy materials to stabilize it. For added safety, place small blocks between the jack cap and load if slipping might occur, but never rely solely on the jack. Confirm the surface is level and solid before lifting to guarantee stable, secure support throughout your work. Assessing ground stability is a crucial step to ensure your safety during vehicle lifting.
Secondary Safety Measures to Prevent Accidents
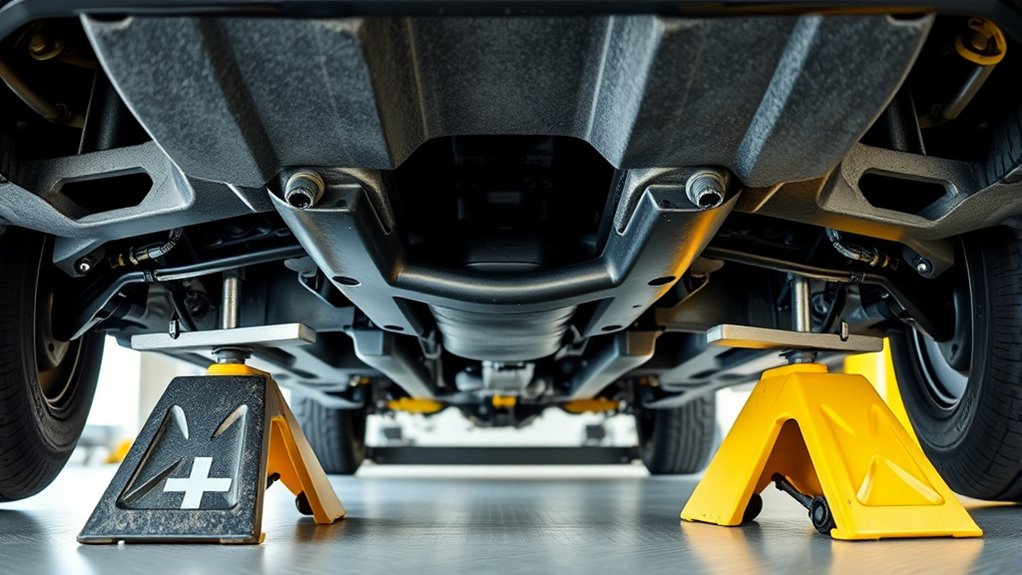

To prevent accidents, always deploy secondary safety measures before working beneath a supported vehicle. Place additional support blocks or rated cribbing under a different structural point, not just the main stands. This acts as a backup if a stand fails or shifts. Keep wheel chocks on the wheels still on the ground to prevent rolling. Lower the vehicle slowly onto the stands, ensuring full contact and stability. Gently nudge the vehicle to check for rocking or movement; if it shifts, reposition the stands. Never rely solely on hydraulic jacks or a single set of stands. Keep the work area clear of bystanders, and double-check all stands are fully engaged, locked, and stable. For extra safety, consider inspecting the essential oils for safety to understand proper handling and precautions. These precautions considerably reduce the risk of sudden collapse or accidents.
Verifying Correct Stand Engagement and Vehicle Stability
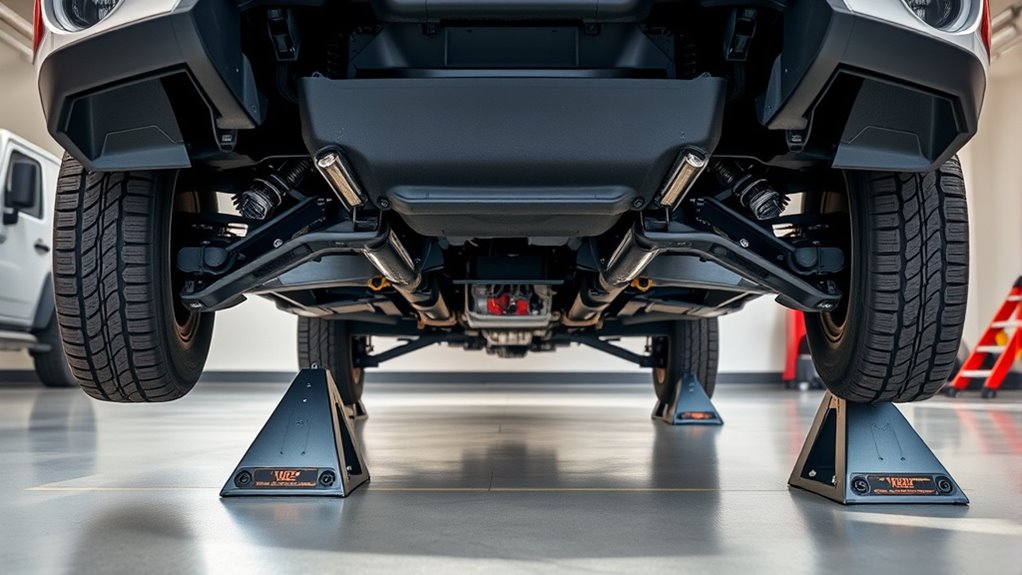

Make sure each stand is fully engaged and stable before working underneath the vehicle. First, check that the locking mechanisms are fully engaged with an audible click and visible pin seating. Next, confirm that all four legs sit flat on a level, solid surface—adjust if any wobbling occurs. Then, verify the stand saddle is centered securely under the load point, preventing lateral slips. You should also perform gentle pushes in all directions to test stability; if any movement occurs, reposition the stands. Keep the floor jack in place as a secondary support if recommended, but remove it once the stands are stable. By following these steps, you ensure the vehicle remains steady and safe during maintenance.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Confirm the Actual Manufacturer-Specified Jack Points on My Vehicle?
You confirm the manufacturer-specified jack points by consulting your vehicle’s owner’s manual, which highlights reinforced lift areas like pinch welds, subframe nodes, or dedicated pads. Look for stamped notches, welded pads, or reinforced plates under the sill or frame. If unsure, avoid improvising; instead, check the factory service manual or contact the dealer to guarantee you’re lifting at the correct, safe locations.
What Signs Indicate a Jack Stand Is Not Properly Engaged or Stable?
You’ll notice if your jack stand isn’t properly engaged if it wobbles or tilts when you gently push the vehicle. Check that the saddle is fully seated on a solid, reinforced part of the chassis or axle. If the stand wobbles, rocks, or feels unstable, reposition it immediately. Always make certain all four legs sit flat on a level surface, and verify the locking mechanism is fully engaged before working underneath.
Can I Use Non-Oem Lift Points for Temporary Support Safely?
No, you shouldn’t use non-OEM lift points for temporary support. You need to trust designated, reinforced locations shown in your vehicle’s manual or on the chassis, such as pinch welds or crossmembers. Using unapproved areas risks damaging the vehicle, causing collapse, or personal injury. Always verify the support point’s strength, ensure stable placement, and double-check that the stands are fully engaged before working underneath.
How Do Ground Conditions Affect the Choice of Jack Stand Placement?
Ground conditions directly influence where you place jack stands. You should always set them on a firm, level surface like concrete or asphalt. Avoid soft, uneven, or sloped ground, which can cause instability or tipping. If necessary, use cribbing or blocks to stabilize the surface. Ensuring a flat, solid base helps evenly distribute weight, reducing the risk of collapse or slipping while supporting your vehicle.
What Are the Risks of Setting Stands at Maximum Extension?
Setting stands at maximum extension is like stretching a rubber band to its limit—you risk snapping it under pressure. When stands are fully extended, the locking pawls engage less securely, increasing the chance of collapse if there’s lateral movement or vibrations. Always keep stands at a comfortable, mid-range height, ensuring full engagement of locking mechanisms, so your support remains stable and safe during maintenance.
Conclusion
By following these proper jack stand placement tips, you’ll considerably reduce the risk of accidents and vehicle damage. Think of your car’s reinforced areas as its skeleton—ignoring them could cause instability. Some say using the wrong lift points is just a minor mistake, but history shows it can lead to serious injuries. When you prioritize safety and double-check your setup, you’re not just lifting a vehicle—you’re protecting yourself and your loved ones.









