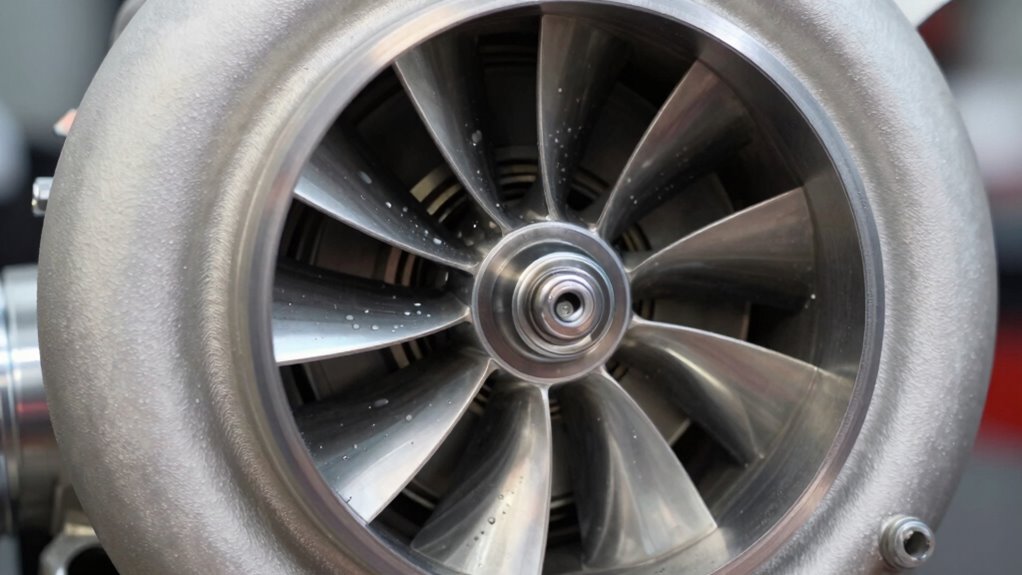
Turbochargers work by capturing energy from your engine’s exhaust gases, spinning a turbine that drives a compressor to force more air into the engine. This compressed air increases oxygen levels, boosting power and efficiency. Designed with advanced materials and aerodynamics, turbochargers optimize heat management and durability. Understanding how these components interact helps improve performance. Keep exploring to uncover the detailed science behind how turbochargers maximize your engine’s potential.
Key Takeaways
- Turbochargers utilize exhaust gases to spin a turbine, which drives a compressor to boost engine air intake.
- The turbine captures high-pressure energy from exhaust flow, converting it into rotational force.
- Compressed air is cooled via intercoolers to improve density and engine efficiency.
- Increased air pressure enhances combustion, resulting in more power without enlarging the engine.
- Material design and heat management are crucial for durability and optimal turbocharger performance.
How Turbochargers Harness Exhaust Energy

Have you ever wondered how turbochargers boost engine power? It all begins with exhaust gas dynamics. When your engine runs, exhaust gases flow rapidly through the exhaust manifold, creating high-pressure energy. This energy is captured by the turbine wheel design inside the turbocharger. As exhaust gases pass over the turbine wheel, they spin it at high speeds. This spinning turbine then drives the compressor wheel, which compresses incoming air and forces more oxygen into your engine. The efficiency of this process depends heavily on the turbine wheel design, which must maximize energy transfer from exhaust gases. turbine wheel design plays a critical role in ensuring optimal performance and durability of the turbocharger. Improving the aerodynamic shape of the turbine wheel can lead to better energy extraction from exhaust gases, further enhancing efficiency. Additionally, advancements in materials used for turbine wheels can improve heat resistance and lifespan. Optimizing the manufacturing processes of turbine wheels can also contribute to more precise and consistent performance. By harnessing exhaust energy this way, turbochargers considerably increase power output without adding extra fuel, making your engine more powerful and efficient.
Components and Design of a Turbocharger
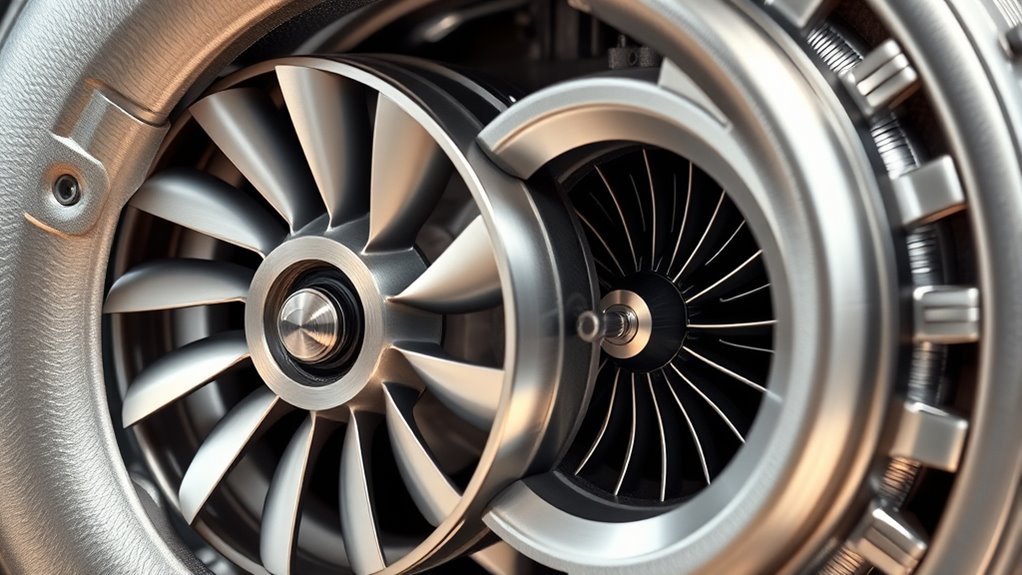

A turbocharger consists of several key components that work together to boost engine performance. The main parts include the turbine, compressor, and central housing. The compressor wheel design is critical because it determines how efficiently air is compressed and delivered to the engine. Materials like titanium or aluminum are used for turbocharger components to balance strength and weight. The compressor wheel’s shape and size influence airflow and pressure ratios, impacting overall efficiency. Proper material selection ensures durability under high-stress conditions and contributes to performance optimization. Additionally, advances in turbocharger technology focus on improving these components for better durability and efficiency, often incorporating advanced materials to enhance performance.
Furthermore, the integration of cooling systems helps maintain optimal operating temperatures, extending the lifespan of turbocharger parts and ensuring consistent performance.
The Thermodynamics of Boosting Air Intake
Understanding the thermodynamics of boosting air intake is vital to grasp how turbochargers enhance engine performance. When the turbocharger compresses air, it increases the air pressure entering the engine, allowing more oxygen to mix with fuel. This process relies on principles of thermodynamics, where compressing air raises its temperature. However, high temperatures can reduce efficiency and cause engine knocking. To counter this, temperature regulation methods, like intercoolers, cool the compressed air before it reaches the cylinders. Cooler air is denser, providing better combustion and power output. The balance of increasing air pressure while managing temperature is indispensable to optimizing engine performance without causing damage or inefficiency. Additionally, advances in thermodynamic efficiency continue to improve turbocharger designs, enabling engines to achieve higher power with lower emissions. For example, heat transfer management techniques are employed to better control temperature and improve overall system performance. Innovative materials and cooling techniques are employed to better manage heat transfer during compression. This delicate thermodynamic process ensures that turbocharged engines deliver more power while maintaining reliability. Moreover, ongoing research in engine thermodynamics helps develop more effective cooling strategies to further enhance performance and durability. As a result, the integration of thermodynamic principles into turbocharger design is crucial for pushing the boundaries of engine efficiency and power output.
Impact on Engine Performance and Efficiency

Turbochargers considerably boost engine performance by increasing the amount of air entering the cylinders, which allows for more fuel to be burned efficiently. This boost pressure enhances power output without enlarging the engine size, making your vehicle more responsive. As a result, you’ll notice improved acceleration and overall drivability. Additionally, higher boost pressure can lead to better fuel economy because the engine works more efficiently, extracting more energy from each drop of fuel. With optimized air intake, your engine can produce more power with less fuel, reducing emissions and saving you money in the long run. Proper air intake management is crucial for maximizing turbocharger benefits and maintaining engine health. Inadequate or poorly managed intake systems can lead to performance issues or engine damage over time. However, maintaining the right balance is vital; too much boost pressure can strain engine components, but when tuned properly, turbochargers greatly impact performance and efficiency positively. Proper turbocharger maintenance ensures sustained performance and longevity of the system. Incorporating analytical thinking into your maintenance routine can help identify potential issues early, preventing costly repairs and ensuring consistent performance.
Common Challenges and Future Developments

While turbochargers offer significant benefits, they also present several challenges that engineers are working to overcome. One key issue is optimizing wastegate function to prevent overboosting or underboosting, which can harm engine longevity. Precise wastegate control helps maintain consistent performance and reduces stress on engine components. Another challenge is improving intercooler efficiency; a more effective intercooler cools compressed air better, increasing power while minimizing heat-related issues. Additionally, integrating Free Floating systems can help improve overall turbocharger responsiveness and adaptability. Innovations in heat management materials are also being explored to better handle the high temperatures generated during operation. Researchers are also exploring thermal insulation to enhance heat retention and management, further supporting turbocharger efficiency. Advances in advanced cooling systems are contributing to better heat dissipation and durability under strenuous conditions. Future developments focus on advanced materials and electronic controls that enhance wastegate responsiveness and intercooler performance. These innovations aim to make turbocharged engines more reliable and efficient, addressing current limitations and paving the way for higher performance, lower emissions, and better fuel economy.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does a Turbocharger Differ From a Supercharger?
A turbocharger differs from a supercharger mainly in how it uses energy. Turbocharger mechanics involve exhaust gases spinning a turbine to boost intake air, making it more efficient. Supercharger differences include being belt-driven off the engine, providing immediate power. You’ll notice turbochargers generally offer better fuel efficiency, while superchargers give instant throttle response. Both increase engine power, but turbochargers work more efficiently at higher speeds.
What Materials Are Used to Build Turbocharger Components?
Did you know that turbocharger components often reach temperatures over 1,000°C? You’ll find that engineers use lightweight composite materials and ceramic components to withstand these extreme conditions. These materials help improve performance and durability, reducing weight and heat stress. By choosing high-quality composites and ceramics, turbochargers can operate efficiently for longer periods, ensuring your vehicle delivers maximum power without compromising reliability.
Can Turbochargers Be Used in Electric Vehicles?
You can’t typically use turbochargers in electric vehicles because electric propulsion doesn’t require internal combustion enhancement. Turbocharger integration is designed to boost traditional engines’ performance, not electric motors. While some concepts explore hybrid systems combining combustion and electric power, pure EVs rely solely on electric motors for propulsion. Consequently, turbochargers aren’t applicable in standard electric vehicles, as their function is unnecessary in an electric propulsion system.
How Does Altitude Affect Turbocharger Performance?
Think of a turbocharger as a windmill harnessing air. At high altitude, thinner air causes an altitude impact, reducing its ability to spin efficiently. This performance variation means your turbo struggles to produce the same boost as at sea level. You’ll notice decreased power and responsiveness, so understanding altitude impact helps you anticipate how your turbocharged engine adapts to different elevations.
What Maintenance Is Required to Ensure Turbocharger Longevity?
To guarantee your turbocharger lasts, you should follow proper lubrication practices by regularly checking and changing the oil, as clean oil reduces wear. Additionally, keep the intake clean by periodically inspecting and cleaning the air filter to prevent debris from damaging the turbine. These steps help maintain peak performance, prevent overheating, and extend the turbocharger’s lifespan, saving you time and costly repairs down the road.
Conclusion
Understanding how turbochargers work helps you appreciate their power and efficiency. Imagine a car owner boosting performance by upgrading to a turbocharged engine, gaining faster acceleration and better fuel economy. Just like in racing, where turbochargers give cars an edge, mastering these components release your vehicle’s true potential. Embracing future innovations means even more impressive gains ahead. So, whether for daily driving or high-speed pursuits, turbochargers can transform your driving experience for the better.






